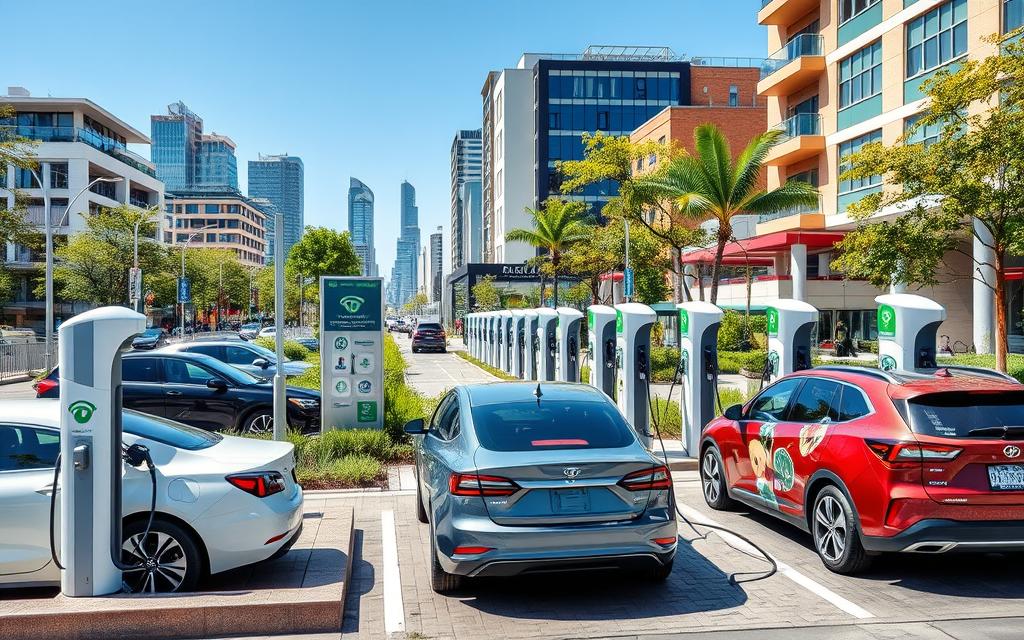
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming more popular. It’s important to know the difference between hybrid and full electric cars. They have different charging needs. We will look at these differences and how they affect charging.
Key Takeaways
- All-electric vehicles can travel 150-400 miles on a full charge, while PHEVs have a range of 15-60 miles on electricity alone.
- All-electric vehicles typically achieve higher fuel economy ratings compared to PHEVs, but both offer significant savings on fuel costs.
- Charging options include home charging, public charging stations, and workplace charging, with varying charging speeds and times.
- Both all-electric vehicles and PHEVs meet federal safety standards and offer environmental benefits through reduced emissions.
- Maintenance requirements differ, with all-electric vehicles generally requiring less maintenance due to fewer moving parts.
Understanding Different Types of Electric Vehicles and Their Charging Needs
The world of electric vehicles (EVs) has many types, each with its own charging needs. As we move towards a greener future, knowing the differences is key. This helps us choose the right EV for our needs.
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) run only on batteries. They are the most popular, with 74% of the market. They can go up to 275 miles on a single charge. But, they need to be charged often, which can take a lot of time.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) mix electric and gasoline power. They make up 13% of the market. They can go about 25 miles on electric alone. Only 14% of them can charge quickly.
Conventional Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) use both an engine and an electric motor. They don’t need to be charged because their batteries get refilled by braking and the engine. But, they can’t use public charging stations for long trips.
As EVs become more common, it’s important to know the differences. This helps us pick the right one for our driving habits, hybrid vs. ev charging needs, battery capacity considerations, and hybrid car charging capabilities. By thinking about these, we can choose what’s best for us and the planet.
EV charging stations for hybrid cars vs full electric cars: Key Differences
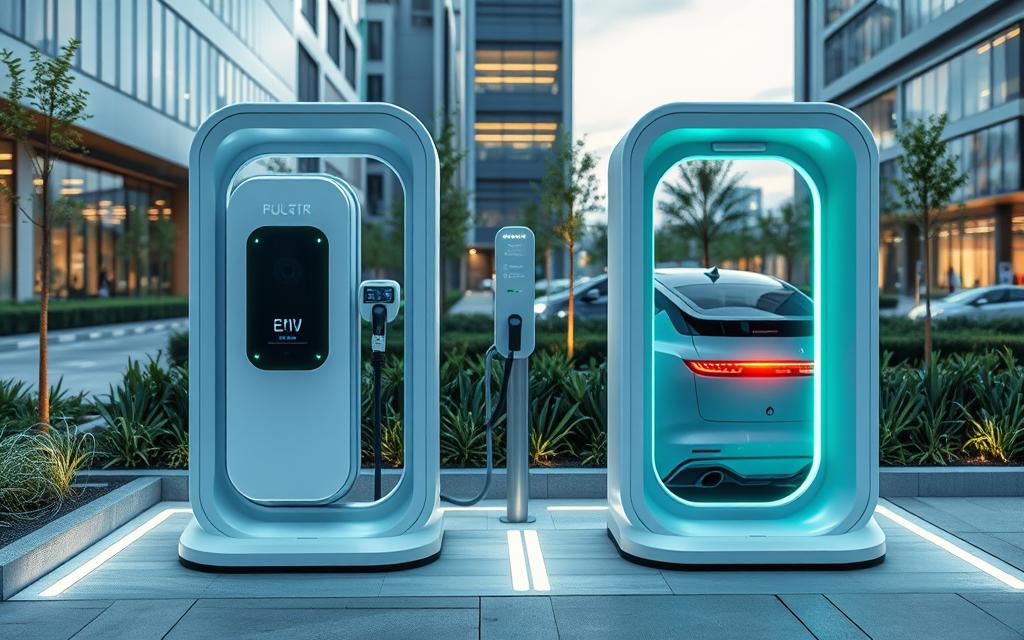

Electric vehicle (EV) charging needs differ for hybrid and full electric cars. It’s important to know these differences for ev charging station compatibility and a good charging experience.
Hybrid cars, or plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), have smaller batteries than full electric cars (BEVs). This means PHEVs need less powerful charging stations. They also charge faster than BEVs. Level 1 charging (120V AC) is good for PHEVs, giving 2-5 miles of range per hour.
BEVs, with their bigger batteries, need more powerful charging stations. Level 2 charging (240V AC) is better for both PHEVs and BEVs, giving 10-20 miles of range per hour. DC Fast Charging is mainly for BEVs, adding 60-80 miles of range in 20 minutes.
The right charging station depends on the car’s battery size and charging needs. Knowing about ev charging station compatibility and charging time differences helps EV owners choose the best charging setup for their hybrid vs electric car charging needs.
Charging Infrastructure and Equipment Types
As more people choose electric vehicles (EVs), we need better charging systems. There are many types of charging, from home setups to public stations. Each has its own benefits.
Level 1 chargers use a regular 120V AC outlet. They’re common in homes and charge slowly. They add about 5 miles of range per hour.
Level 2 chargers work at 240V AC. They charge faster, adding about 25 miles per hour. They’re great for both home and public use.
Public stations often have DC Fast Charge (DCFC) stations. They can charge up to 200+ miles in 30 minutes. These fast chargers are perfect for long trips or when you’re in a hurry.
Charging time varies a lot. It can be as short as 20 minutes with a DC Fast Charger. Or it can take over 20 hours with a Level 1 charger. Knowing this helps EV owners plan their charging.
As charging tech improves, we’ll see more public stations and better integration with our transportation systems.
Cost Analysis: Charging Hybrid vs Full Electric Vehicles
Looking at the cost of charging hybrid and full electric vehicles, we see a few key points. Electric vehicles (EVs) might cost more upfront. But, they often cost less to run than cars that use gasoline.
The cost to charge an EV can be as low as $0.02 to $0.10 per mile. This is much cheaper than the $0.04 to $0.36 per mile for gasoline. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) can use electricity or gasoline. This can help lower your fuel costs.
EVs also have lower maintenance costs because they have fewer parts. This adds to the long-term savings. You can get up to $7,500 in federal tax credits for new electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles. Some states, like New York, offer extra incentives like the Drive Clean Rebate.
Choosing between a hybrid or a full electric vehicle affects your fuel and operating costs. Think about your driving habits, charging access, and incentives. This can help you save money over time.
The cost of charging hybrid vs electric vehicles depends on many things. These include your driving, charging station access, and incentives. Knowing these factors helps you choose the best option for your budget and needs.
Range Considerations and Charging Frequency
Exploring electric vehicles (EVs) means knowing about range and charging. Battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) can go 150-400 miles on one charge. Some go over 400 miles. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) can go 15-60 miles electric before needing gas.
Driving conditions like weather and how you drive affect the range. BEVs need more frequent charging because they run on batteries. PHEVs use gas when the battery runs out, making them less stressful to drive.
Charging frequency varies based on how far you drive, charging spots, and how you use your car. Thanks to new tech, EVs will soon have longer ranges and faster charging times. Better batteries, cooling systems, and more charging spots will make driving EVs better.
As we move towards a greener future, knowing about EV ranges and charging is key. It helps make driving EVs smooth and worry-free for everyone.
Home and Public Charging Station Accessibility
More people are choosing electric vehicles (EVs), making charging solutions key. Home charging is often the best and cheapest choice. Level 2 chargers at home can charge cars overnight, saving time.
The U.S. government helps by offering tax credits for home chargers. These credits can cover up to 30% of costs, up to $1,000. This makes charging at home more affordable for many.
Public charging stations are also growing. You can find them at work, malls, and highways. Apps and websites help find these stations easily.
Some jobs offer charging for employees too. As EVs become more popular, these charging spots are vital. They help make electric cars a common choice for travel.
Conclusion
Hybrid and fully electric vehicles are great for our planet. They help cut down on carbon emissions and make our environment cleaner. Hybrid cars are cheaper to buy, but electric vehicles save money over time because they need less maintenance and fuel.
Electric cars don’t pollute because they don’t have a tailpipe. But, they cost more to buy and might not go as far on a charge. Yet, as charging gets faster and more places offer it, electric cars will become even more appealing.
Choosing between hybrid and electric cars depends on what you need and where you can charge. Both types help us use less gas and reduce pollution. As technology improves, we’ll see even better options for clean, efficient travel.
FAQ
What are the key differences between EV charging stations for hybrid cars vs. full electric cars?
What are the different types of electric vehicles and how do their charging needs vary?
How compatible are EV charging stations with different types of electric vehicles?
What are the main types of EV charging equipment and how do they differ in terms of charging time?
How do the costs of charging hybrid vs. full electric vehicles compare?
FAQ
What are the key differences between EV charging stations for hybrid cars vs. full electric cars?
Charging stations for hybrid and full electric cars differ in power and speed. Hybrid cars charge faster because they have smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the different types of electric vehicles and how do their charging needs vary?
Electric vehicles include all-electric and plug-in hybrid cars. All-electric cars need regular charging. Plug-in hybrids can use both electricity and gasoline, offering more flexibility.
Charging needs depend on the vehicle type. All-electric cars need more frequent and longer charging than plug-in hybrids.
How compatible are EV charging stations with different types of electric vehicles?
Compatibility with EV charging stations varies by vehicle and equipment. Hybrid cars charge faster with smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the main types of EV charging equipment and how do they differ in terms of charging time?
EV charging includes Level 1 (120V AC), Level 2 (240V AC), and DC Fast Charging (480V AC). Charging times range from 20 minutes (DC Fast Charge) to over 20 hours (Level 1). It depends on the method and battery size.
How do the costs of charging hybrid vs. full electric vehicles compare?
Electric vehicles cost more upfront but less to run. Charging costs
FAQ
What are the key differences between EV charging stations for hybrid cars vs. full electric cars?
Charging stations for hybrid and full electric cars differ in power and speed. Hybrid cars charge faster because they have smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the different types of electric vehicles and how do their charging needs vary?
Electric vehicles include all-electric and plug-in hybrid cars. All-electric cars need regular charging. Plug-in hybrids can use both electricity and gasoline, offering more flexibility.
Charging needs depend on the vehicle type. All-electric cars need more frequent and longer charging than plug-in hybrids.
How compatible are EV charging stations with different types of electric vehicles?
Compatibility with EV charging stations varies by vehicle and equipment. Hybrid cars charge faster with smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the main types of EV charging equipment and how do they differ in terms of charging time?
EV charging includes Level 1 (120V AC), Level 2 (240V AC), and DC Fast Charging (480V AC). Charging times range from 20 minutes (DC Fast Charge) to over 20 hours (Level 1). It depends on the method and battery size.
How do the costs of charging hybrid vs. full electric vehicles compare?
Electric vehicles cost more upfront but less to run. Charging costs $0.02 to $0.10 per mile. Gasoline costs $0.04 to $0.36 per mile.
PHEVs offer flexibility in fuel choices, which can lower costs. BEVs have lower maintenance costs due to fewer parts.
What are the range considerations and charging frequency differences between hybrid and full electric vehicles?
BEVs have ranges of 150-400 miles on a full charge. PHEVs have electric-only ranges of 15-60 miles before using gasoline. Driving conditions affect actual range.
BEVs need more frequent charging than PHEVs because they rely on batteries.
How accessible are home and public charging stations for electric and hybrid vehicle owners?
Home charging is often the most convenient and cost-effective option. Level 2 chargers charge faster. Public charging is growing, with stations at workplaces, shopping centers, and highways.
Some workplaces offer charging for employees.
FAQ
What are the key differences between EV charging stations for hybrid cars vs. full electric cars?
Charging stations for hybrid and full electric cars differ in power and speed. Hybrid cars charge faster because they have smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the different types of electric vehicles and how do their charging needs vary?
Electric vehicles include all-electric and plug-in hybrid cars. All-electric cars need regular charging. Plug-in hybrids can use both electricity and gasoline, offering more flexibility.
Charging needs depend on the vehicle type. All-electric cars need more frequent and longer charging than plug-in hybrids.
How compatible are EV charging stations with different types of electric vehicles?
Compatibility with EV charging stations varies by vehicle and equipment. Hybrid cars charge faster with smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the main types of EV charging equipment and how do they differ in terms of charging time?
EV charging includes Level 1 (120V AC), Level 2 (240V AC), and DC Fast Charging (480V AC). Charging times range from 20 minutes (DC Fast Charge) to over 20 hours (Level 1). It depends on the method and battery size.
How do the costs of charging hybrid vs. full electric vehicles compare?
Electric vehicles cost more upfront but less to run. Charging costs
FAQ
What are the key differences between EV charging stations for hybrid cars vs. full electric cars?
Charging stations for hybrid and full electric cars differ in power and speed. Hybrid cars charge faster because they have smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the different types of electric vehicles and how do their charging needs vary?
Electric vehicles include all-electric and plug-in hybrid cars. All-electric cars need regular charging. Plug-in hybrids can use both electricity and gasoline, offering more flexibility.
Charging needs depend on the vehicle type. All-electric cars need more frequent and longer charging than plug-in hybrids.
How compatible are EV charging stations with different types of electric vehicles?
Compatibility with EV charging stations varies by vehicle and equipment. Hybrid cars charge faster with smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the main types of EV charging equipment and how do they differ in terms of charging time?
EV charging includes Level 1 (120V AC), Level 2 (240V AC), and DC Fast Charging (480V AC). Charging times range from 20 minutes (DC Fast Charge) to over 20 hours (Level 1). It depends on the method and battery size.
How do the costs of charging hybrid vs. full electric vehicles compare?
Electric vehicles cost more upfront but less to run. Charging costs $0.02 to $0.10 per mile. Gasoline costs $0.04 to $0.36 per mile.
PHEVs offer flexibility in fuel choices, which can lower costs. BEVs have lower maintenance costs due to fewer parts.
What are the range considerations and charging frequency differences between hybrid and full electric vehicles?
BEVs have ranges of 150-400 miles on a full charge. PHEVs have electric-only ranges of 15-60 miles before using gasoline. Driving conditions affect actual range.
BEVs need more frequent charging than PHEVs because they rely on batteries.
How accessible are home and public charging stations for electric and hybrid vehicle owners?
Home charging is often the most convenient and cost-effective option. Level 2 chargers charge faster. Public charging is growing, with stations at workplaces, shopping centers, and highways.
Some workplaces offer charging for employees.
FAQ
What are the key differences between EV charging stations for hybrid cars vs. full electric cars?
Charging stations for hybrid and full electric cars differ in power and speed. Hybrid cars charge faster because they have smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the different types of electric vehicles and how do their charging needs vary?
Electric vehicles include all-electric and plug-in hybrid cars. All-electric cars need regular charging. Plug-in hybrids can use both electricity and gasoline, offering more flexibility.
Charging needs depend on the vehicle type. All-electric cars need more frequent and longer charging than plug-in hybrids.
How compatible are EV charging stations with different types of electric vehicles?
Compatibility with EV charging stations varies by vehicle and equipment. Hybrid cars charge faster with smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the main types of EV charging equipment and how do they differ in terms of charging time?
EV charging includes Level 1 (120V AC), Level 2 (240V AC), and DC Fast Charging (480V AC). Charging times range from 20 minutes (DC Fast Charge) to over 20 hours (Level 1). It depends on the method and battery size.
How do the costs of charging hybrid vs. full electric vehicles compare?
Electric vehicles cost more upfront but less to run. Charging costs
FAQ
What are the key differences between EV charging stations for hybrid cars vs. full electric cars?
Charging stations for hybrid and full electric cars differ in power and speed. Hybrid cars charge faster because they have smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the different types of electric vehicles and how do their charging needs vary?
Electric vehicles include all-electric and plug-in hybrid cars. All-electric cars need regular charging. Plug-in hybrids can use both electricity and gasoline, offering more flexibility.
Charging needs depend on the vehicle type. All-electric cars need more frequent and longer charging than plug-in hybrids.
How compatible are EV charging stations with different types of electric vehicles?
Compatibility with EV charging stations varies by vehicle and equipment. Hybrid cars charge faster with smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the main types of EV charging equipment and how do they differ in terms of charging time?
EV charging includes Level 1 (120V AC), Level 2 (240V AC), and DC Fast Charging (480V AC). Charging times range from 20 minutes (DC Fast Charge) to over 20 hours (Level 1). It depends on the method and battery size.
How do the costs of charging hybrid vs. full electric vehicles compare?
Electric vehicles cost more upfront but less to run. Charging costs $0.02 to $0.10 per mile. Gasoline costs $0.04 to $0.36 per mile.
PHEVs offer flexibility in fuel choices, which can lower costs. BEVs have lower maintenance costs due to fewer parts.
What are the range considerations and charging frequency differences between hybrid and full electric vehicles?
BEVs have ranges of 150-400 miles on a full charge. PHEVs have electric-only ranges of 15-60 miles before using gasoline. Driving conditions affect actual range.
BEVs need more frequent charging than PHEVs because they rely on batteries.
How accessible are home and public charging stations for electric and hybrid vehicle owners?
Home charging is often the most convenient and cost-effective option. Level 2 chargers charge faster. Public charging is growing, with stations at workplaces, shopping centers, and highways.
Some workplaces offer charging for employees.
FAQ
What are the key differences between EV charging stations for hybrid cars vs. full electric cars?
Charging stations for hybrid and full electric cars differ in power and speed. Hybrid cars charge faster because they have smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the different types of electric vehicles and how do their charging needs vary?
Electric vehicles include all-electric and plug-in hybrid cars. All-electric cars need regular charging. Plug-in hybrids can use both electricity and gasoline, offering more flexibility.
Charging needs depend on the vehicle type. All-electric cars need more frequent and longer charging than plug-in hybrids.
How compatible are EV charging stations with different types of electric vehicles?
Compatibility with EV charging stations varies by vehicle and equipment. Hybrid cars charge faster with smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the main types of EV charging equipment and how do they differ in terms of charging time?
EV charging includes Level 1 (120V AC), Level 2 (240V AC), and DC Fast Charging (480V AC). Charging times range from 20 minutes (DC Fast Charge) to over 20 hours (Level 1). It depends on the method and battery size.
How do the costs of charging hybrid vs. full electric vehicles compare?
Electric vehicles cost more upfront but less to run. Charging costs
FAQ
What are the key differences between EV charging stations for hybrid cars vs. full electric cars?
Charging stations for hybrid and full electric cars differ in power and speed. Hybrid cars charge faster because they have smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the different types of electric vehicles and how do their charging needs vary?
Electric vehicles include all-electric and plug-in hybrid cars. All-electric cars need regular charging. Plug-in hybrids can use both electricity and gasoline, offering more flexibility.
Charging needs depend on the vehicle type. All-electric cars need more frequent and longer charging than plug-in hybrids.
How compatible are EV charging stations with different types of electric vehicles?
Compatibility with EV charging stations varies by vehicle and equipment. Hybrid cars charge faster with smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the main types of EV charging equipment and how do they differ in terms of charging time?
EV charging includes Level 1 (120V AC), Level 2 (240V AC), and DC Fast Charging (480V AC). Charging times range from 20 minutes (DC Fast Charge) to over 20 hours (Level 1). It depends on the method and battery size.
How do the costs of charging hybrid vs. full electric vehicles compare?
Electric vehicles cost more upfront but less to run. Charging costs $0.02 to $0.10 per mile. Gasoline costs $0.04 to $0.36 per mile.
PHEVs offer flexibility in fuel choices, which can lower costs. BEVs have lower maintenance costs due to fewer parts.
What are the range considerations and charging frequency differences between hybrid and full electric vehicles?
BEVs have ranges of 150-400 miles on a full charge. PHEVs have electric-only ranges of 15-60 miles before using gasoline. Driving conditions affect actual range.
BEVs need more frequent charging than PHEVs because they rely on batteries.
How accessible are home and public charging stations for electric and hybrid vehicle owners?
Home charging is often the most convenient and cost-effective option. Level 2 chargers charge faster. Public charging is growing, with stations at workplaces, shopping centers, and highways.
Some workplaces offer charging for employees.
.02 to
FAQ
What are the key differences between EV charging stations for hybrid cars vs. full electric cars?
Charging stations for hybrid and full electric cars differ in power and speed. Hybrid cars charge faster because they have smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the different types of electric vehicles and how do their charging needs vary?
Electric vehicles include all-electric and plug-in hybrid cars. All-electric cars need regular charging. Plug-in hybrids can use both electricity and gasoline, offering more flexibility.
Charging needs depend on the vehicle type. All-electric cars need more frequent and longer charging than plug-in hybrids.
How compatible are EV charging stations with different types of electric vehicles?
Compatibility with EV charging stations varies by vehicle and equipment. Hybrid cars charge faster with smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the main types of EV charging equipment and how do they differ in terms of charging time?
EV charging includes Level 1 (120V AC), Level 2 (240V AC), and DC Fast Charging (480V AC). Charging times range from 20 minutes (DC Fast Charge) to over 20 hours (Level 1). It depends on the method and battery size.
How do the costs of charging hybrid vs. full electric vehicles compare?
Electric vehicles cost more upfront but less to run. Charging costs $0.02 to $0.10 per mile. Gasoline costs $0.04 to $0.36 per mile.
PHEVs offer flexibility in fuel choices, which can lower costs. BEVs have lower maintenance costs due to fewer parts.
What are the range considerations and charging frequency differences between hybrid and full electric vehicles?
BEVs have ranges of 150-400 miles on a full charge. PHEVs have electric-only ranges of 15-60 miles before using gasoline. Driving conditions affect actual range.
BEVs need more frequent charging than PHEVs because they rely on batteries.
How accessible are home and public charging stations for electric and hybrid vehicle owners?
Home charging is often the most convenient and cost-effective option. Level 2 chargers charge faster. Public charging is growing, with stations at workplaces, shopping centers, and highways.
Some workplaces offer charging for employees.
.10 per mile. Gasoline costs
FAQ
What are the key differences between EV charging stations for hybrid cars vs. full electric cars?
Charging stations for hybrid and full electric cars differ in power and speed. Hybrid cars charge faster because they have smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the different types of electric vehicles and how do their charging needs vary?
Electric vehicles include all-electric and plug-in hybrid cars. All-electric cars need regular charging. Plug-in hybrids can use both electricity and gasoline, offering more flexibility.
Charging needs depend on the vehicle type. All-electric cars need more frequent and longer charging than plug-in hybrids.
How compatible are EV charging stations with different types of electric vehicles?
Compatibility with EV charging stations varies by vehicle and equipment. Hybrid cars charge faster with smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the main types of EV charging equipment and how do they differ in terms of charging time?
EV charging includes Level 1 (120V AC), Level 2 (240V AC), and DC Fast Charging (480V AC). Charging times range from 20 minutes (DC Fast Charge) to over 20 hours (Level 1). It depends on the method and battery size.
How do the costs of charging hybrid vs. full electric vehicles compare?
Electric vehicles cost more upfront but less to run. Charging costs $0.02 to $0.10 per mile. Gasoline costs $0.04 to $0.36 per mile.
PHEVs offer flexibility in fuel choices, which can lower costs. BEVs have lower maintenance costs due to fewer parts.
What are the range considerations and charging frequency differences between hybrid and full electric vehicles?
BEVs have ranges of 150-400 miles on a full charge. PHEVs have electric-only ranges of 15-60 miles before using gasoline. Driving conditions affect actual range.
BEVs need more frequent charging than PHEVs because they rely on batteries.
How accessible are home and public charging stations for electric and hybrid vehicle owners?
Home charging is often the most convenient and cost-effective option. Level 2 chargers charge faster. Public charging is growing, with stations at workplaces, shopping centers, and highways.
Some workplaces offer charging for employees.
.04 to
FAQ
What are the key differences between EV charging stations for hybrid cars vs. full electric cars?
Charging stations for hybrid and full electric cars differ in power and speed. Hybrid cars charge faster because they have smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the different types of electric vehicles and how do their charging needs vary?
Electric vehicles include all-electric and plug-in hybrid cars. All-electric cars need regular charging. Plug-in hybrids can use both electricity and gasoline, offering more flexibility.
Charging needs depend on the vehicle type. All-electric cars need more frequent and longer charging than plug-in hybrids.
How compatible are EV charging stations with different types of electric vehicles?
Compatibility with EV charging stations varies by vehicle and equipment. Hybrid cars charge faster with smaller batteries. Full electric cars need more powerful stations for their big batteries.
What are the main types of EV charging equipment and how do they differ in terms of charging time?
EV charging includes Level 1 (120V AC), Level 2 (240V AC), and DC Fast Charging (480V AC). Charging times range from 20 minutes (DC Fast Charge) to over 20 hours (Level 1). It depends on the method and battery size.
How do the costs of charging hybrid vs. full electric vehicles compare?
Electric vehicles cost more upfront but less to run. Charging costs $0.02 to $0.10 per mile. Gasoline costs $0.04 to $0.36 per mile.
PHEVs offer flexibility in fuel choices, which can lower costs. BEVs have lower maintenance costs due to fewer parts.
What are the range considerations and charging frequency differences between hybrid and full electric vehicles?
BEVs have ranges of 150-400 miles on a full charge. PHEVs have electric-only ranges of 15-60 miles before using gasoline. Driving conditions affect actual range.
BEVs need more frequent charging than PHEVs because they rely on batteries.
How accessible are home and public charging stations for electric and hybrid vehicle owners?
Home charging is often the most convenient and cost-effective option. Level 2 chargers charge faster. Public charging is growing, with stations at workplaces, shopping centers, and highways.
Some workplaces offer charging for employees.
.36 per mile.
PHEVs offer flexibility in fuel choices, which can lower costs. BEVs have lower maintenance costs due to fewer parts.
What are the range considerations and charging frequency differences between hybrid and full electric vehicles?
BEVs have ranges of 150-400 miles on a full charge. PHEVs have electric-only ranges of 15-60 miles before using gasoline. Driving conditions affect actual range.
BEVs need more frequent charging than PHEVs because they rely on batteries.
How accessible are home and public charging stations for electric and hybrid vehicle owners?
Home charging is often the most convenient and cost-effective option. Level 2 chargers charge faster. Public charging is growing, with stations at workplaces, shopping centers, and highways.
Some workplaces offer charging for employees.


